Common Communication Protocols
Last Updated On July • 8 min read
What Are Communication Protocols?
Communication protocols are the languages that allow devices to share data. In weighing and force measurement systems, they define how signals from load cells, other sensors, indicators, and transmitters are formatted, transmitted, and interpreted by controllers, PLCs, or data acquisition systems. These protocols ensure compatibility between components, reduce errors in data transfer, and allow for integration with larger automation and control networks.
Choosing the right protocol is essential for integrating scales and measurement devices into larger process control systems. Whether you are building an automated batching line, a remote monitoring setup, or a PLC-controlled weighing station, communication protocols ensure accurate, reliable, and efficient data exchange between all components.
Content:
- Why Communication Protocols Matter in Weighing Systems
- Overview of Common Weighing Communication Protocol
- Comparison Table of Communication Protocols in Weighing Systems
- Final Thoughts: Choosing the Best Communication Protocol for Your Weighing System
- ANYLOAD Products with Communication Protocol Support
- Need Help Choosing the Right Protocol?
Why Communication Protocols Matter in Weighing Systems
In any digital weighing system, communication protocols are the backbone of how load cells, weighing indicators, amplifiers, and industrial controllers talk to each other. Choosing the right protocol impacts:
- Data accuracy and update rate
- System scalability
- Integration with PLCs, SCADA, or cloud systems
- Cost and reliability
Whether you’re configuring a truck scale, batching plant, platform scale, or dynamic weighing system, understanding the different protocols is critical for system performance.
Overview of Common Weighing Communication Protocol
 +
+
RS-232: Simple and Time-Tested Serial Communication
RS-232 is one of the earliest serial communication standards used in weighing systems. Features- Distance: Up to 15 meters
- Speed: 9600 – 115200 bps
- Topology: Point-to-point (1:1)
- Wiring: 3 wires (TX, RX, GND)
- Connecting an indicator to a PC
- Serial printing from scales
- Calibration interface
- Easy to implement and debug
- Low cost
- One-to-one only
- Limited noise immunity
 +
+
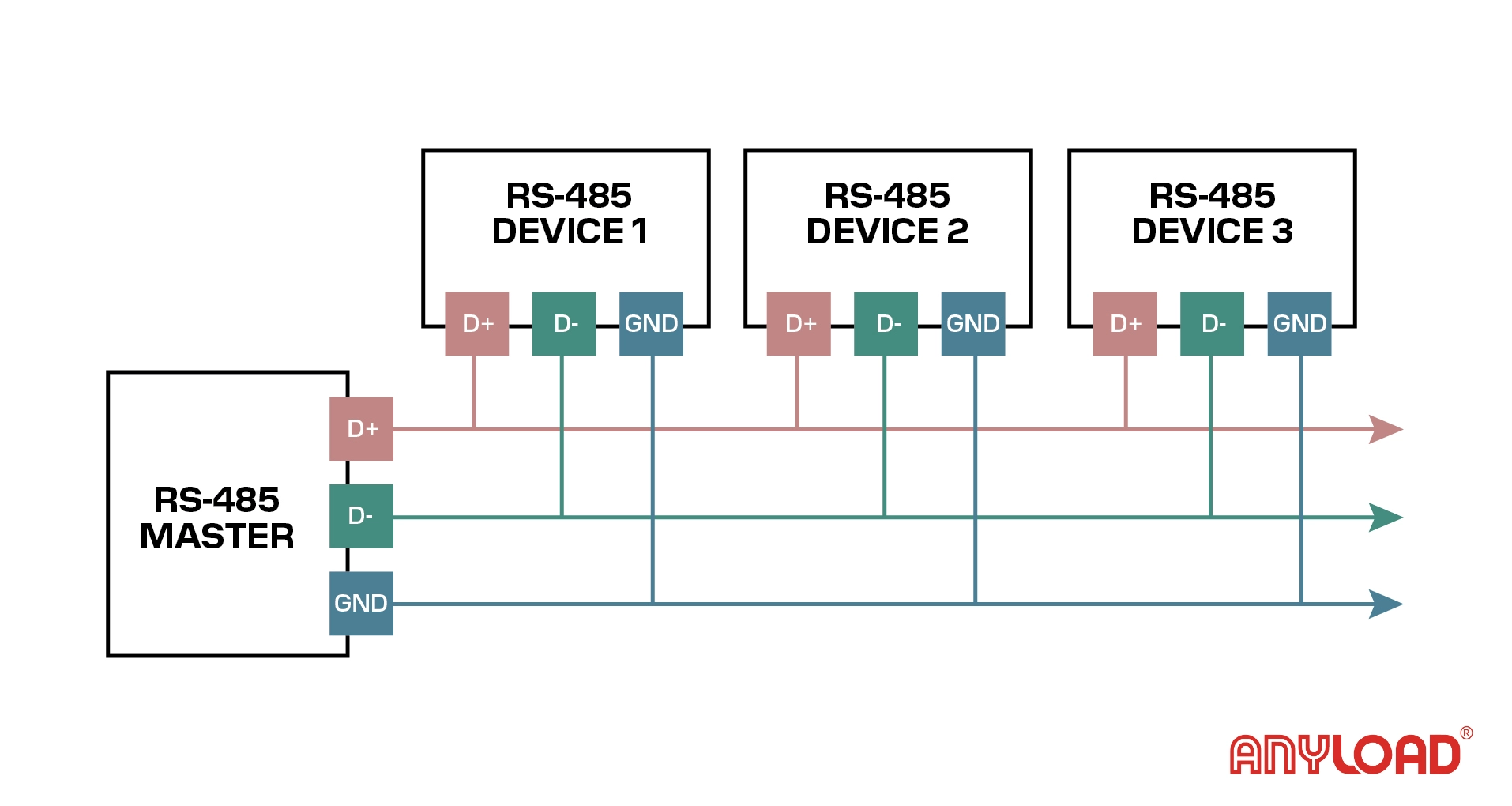
RS-485: The Industrial Workhorse for Multi-Drop Systems
RS-485 allows multiple devices to share the same two-wire communication line.
Features
- Distance: Up to 1200 meters
- Speed: Up to 10 Mbps
- Supports up to 32 devices
Use Cases
- Multi-sensor weighing systems
- Load cell junction boxes
- Long-distance installations
Pros
- High noise immunity
- Robust for harsh environments
Cons
- Requires termination and proper grounding
MODBUS RTU & TCP: A Universal Industrial Protocol
MODBUS is an application-layer protocol widely adopted in PLC and SCADA systems. It can run over RS-485 (RTU) or Ethernet (TCP/IP).
Features
- Master-slave or client-server
- Standard register-based structure
Use Cases
- Process weighing with PLCs
- Tank level monitoring
- SCADA integration
Pros
- Open standard, widely supported
- Scalable from small systems to plant-wide networks
Cons
- RTU requires strict timing
- No native device discovery
 +
+
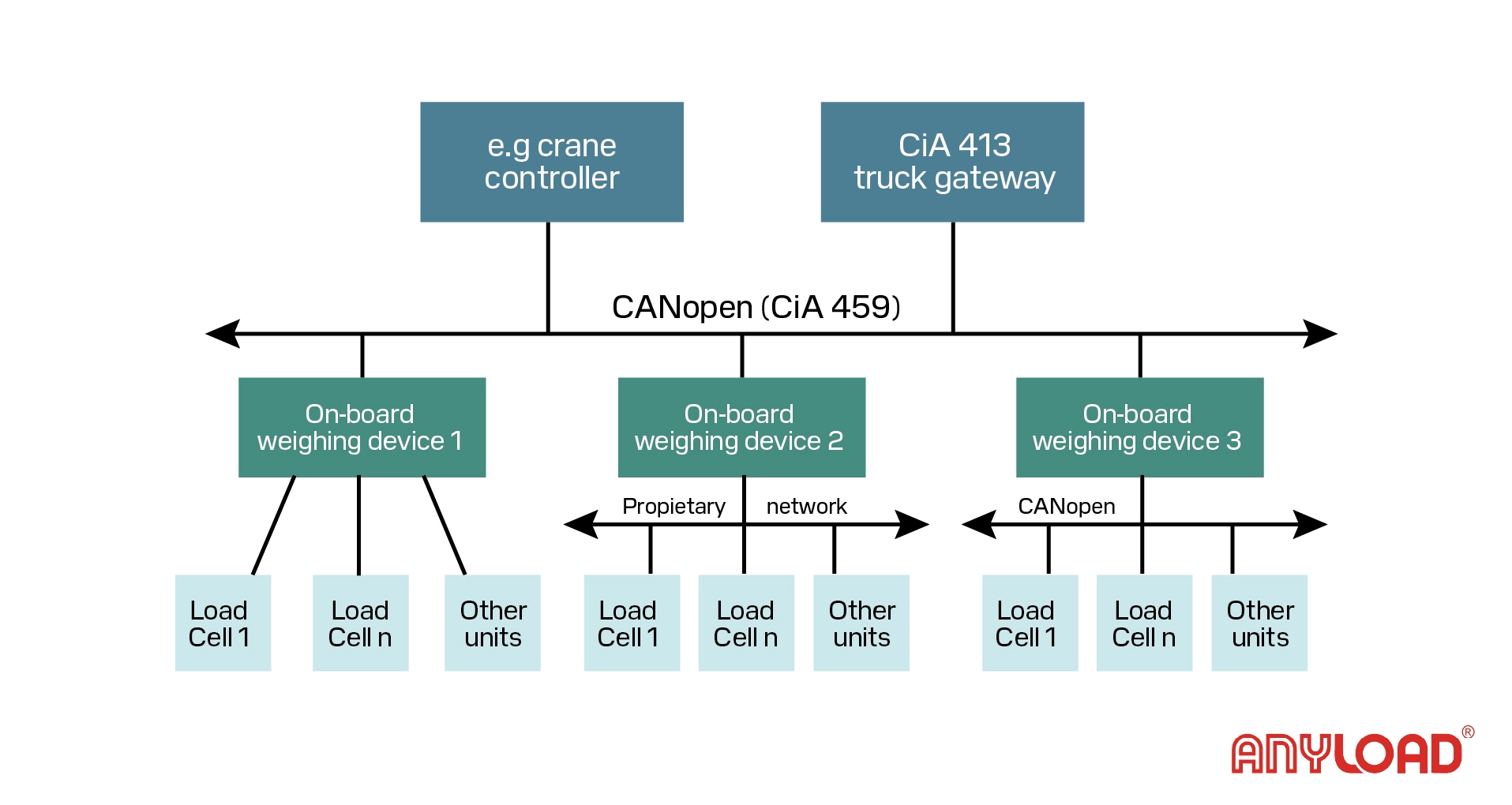
CANopen: Real-Time Precision and Full Device Control
CANopen is a real-time communication protocol designed for high-performance industrial applications.
Why CANopen Stands Out
- PDOs (Process Data Objects) for fast data
- SDOs (Service Data Objects) for configuration and diagnostics
- Based on CiA 404 standard for weighing devices
Key Benefits
- Fast updates and low latency
- Deterministic communication
- Built-in device discovery
- Supports advanced calibration and diagnostics
Use Cases
- High-speed force measurement
- Modular weighing solutions
- OEM weighing systems
Cons
- RTU requires strict timing
- No native device discovery
Ethernet (TCP/IP): High-Speed Industrial Connectivity
Ethernet brings networking to the world of weighing with standard IP protocols.
Features
- Speed: 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps
- Integration with IT/OT networks
- Supports MODBUS TCP, FTP, HTTP
Use Cases
- Remote scale monitoring
- Cloud-connected indicators
- Web-based diagnostics
Pros
- Long-distance and high-speed
- Easily integrates with industrial PCs
Cons
- Requires more power
- More expensive hardware
Wireless (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi & Cellular): Flexible, Cable-Free Integration
Wireless protocols improve mobility and simplify installation, but each has trade-offs in range, reliability, and infrastructure needs.
Bluetooth
Ideal for handheld indicators or mobile apps with short-range connections.
✔ Simple setup for local use
✖ Limited range and potential interference in industrial environments
Wi-Fi
Supports wireless weight transmission, local network integration, or cloud logging.
✔ Good for in-plant monitoring and data access
✖ Requires stable network infrastructure and security management
Cellular (3G/4G/LTE)
Used in remote or mobile weighing setups without fixed connectivity.
✔ Enables long-range communication for isolated or mobile systems
✖ Dependent on coverage area and data plan costs
 +
+
Analog Output (0–10V, 4–20mA): Simple and PLC-Compatible
Analog outputs remain in use for compatibility with legacy PLC systems and signal conditioners.
Use Cases
- Feedback loops
- Redundant analog backup
- Analog-only PLC inputs
Comparison Table of Communication Protocols in Weighing Systems
| Protocol | Distance | Speed | Devices | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS-232 | Short | Low | 1 | Calibration & simple data output |
| RS-485 | Long | Medium | 32+ | Multi-sensor wired systems |
| MODBUS RTU | Long | Medium | Many | PLC/SCADA integration |
| CANopen | Medium | High | Many | Smart modular weighing networks |
| Ethernet | Very Long | Very High | Many | Cloud or remote access |
| Bluetooth | Short | Medium | Few | Mobile diagnostics or field apps |
| Wi-Fi | Long | High | Many | Wireless industrial connectivity |
| Analog | Long | N/A | 1 | Legacy PLC or signal replication |
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Best Communication Protocol for Your Weighing System
Each protocol brings a balance of cost, complexity, distance, and performance. For scalable, real-time, and intelligent weighing solutions, CANopen stands out with its built-in object dictionary, robust diagnostics, and industry-standard CiA 404 profile.
When selecting a protocol:
- Match it to your data rate and latency needs
- Consider integration with PLCs, cloud, or SCADA
- Think about system expansion or modularity
ANYLOAD Products with Communication Protocol Support
ANYLOAD offers a range of devices designed to allow load cells (and all Wheatstone-bridge-based sensors) to interface with modern control systems using industry-standard communication protocols:
- Digital Amplifier Boards (DGB Series):
Compact signal conditioners that support RS-485 (Modbus RTU), RS-232, CANopen, and analog (mV/V or 4–20 mA) outputs. Ideal for retrofitting analog load cells into digital systems or integrating with PLCs and DAQs. - ACT1 Transmitter Series:
A versatile field-mount transmitter available with Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP (Ethernet), CANopen, analog, PROFINET, PROFIBUS, and other output options. Designed for industrial and outdoor environments, the ACT1 enables direct connection between load cells and automation or monitoring systems. - AN310 Panel-Mount Indicator:
A multifunctional weighing display with support for RS-232, RS-485, Modbus RTU, Ethernet TCP/IP, and analog output. Suitable for control panel integration in batching, filling, and general industrial applications.
These products help bridge the gap between precision load cell measurements and broader system controls, ensuring seamless data flow in wired or wireless setups.
Need Help Choosing the Right Protocol?
We specialize in load cell integration, digital amplifier communications, and custom protocol configurations for industrial weighing applications.
Contact us today to build a smarter, more connected weighing system.